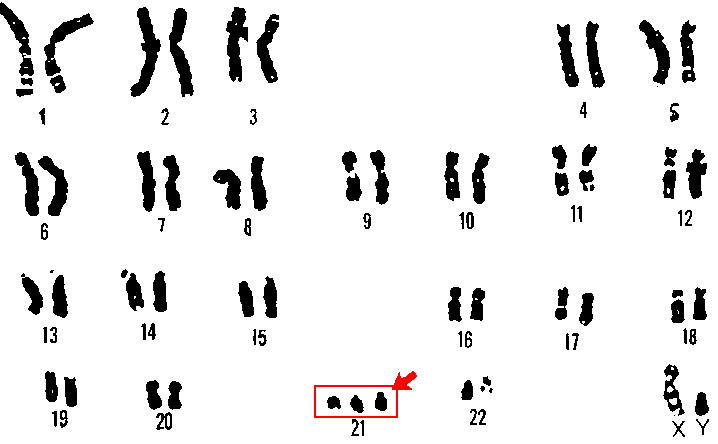
Down syndrome is caused by an extra copy of the 21st chromosome in a person's cells, known as trisomy 21. This means that, instead of having two copies of chromosome 21, they have three copies (pictured below). In rare cases, the extra copy may not be present in every cell — a condition known as mosaic down syndrome. People with mosaic Down syndrome have milder symptoms and a longer life expectancy. There is no clear cause for trisomy 21, although maternal age can be a risk factor.
People with Down syndrome are at a higher risk of developing early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Chromosome 21 contains the gene that codes for the amyloid precursor protein (APP). This is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, and therefore possessing an extra copy of the gene increases the chance of developing early-onset Alzheimer's.
There are no cures or treatments for Down syndrome. However, therapy can improve the condition of life. Researchers are looking into Barr bodies (inactive X-chromosomes) as a way of silencing the extra copy of chromosome 21.
________
Image Credit:
(1) “Trisomy 21.” Wikimedia Commons, 5 Oct. 2006, upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/ab/21_trisomy_-_Down_syndrome.png.
Comments
Post a Comment